16tgrs(3dcnn)Deep Feature Extraction and Classification of Hyperspectral Images Based on Convolutional Neural Networks
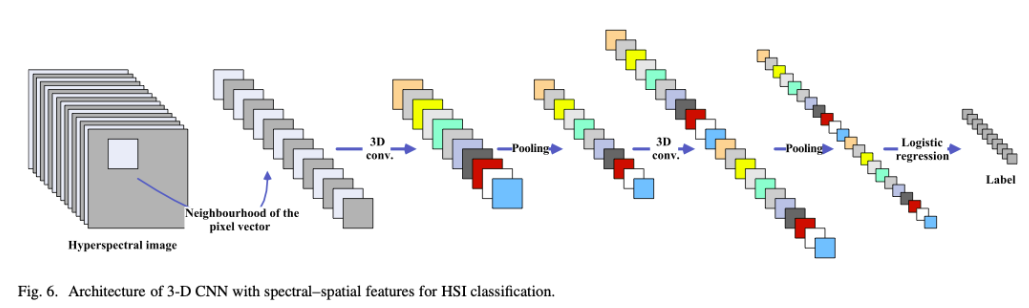
整体流程
3D-CNN
在第$i$层第$j$个特征图的位置$(x,y,z)$处神经元的值$v_{i,j}^{xyz}$
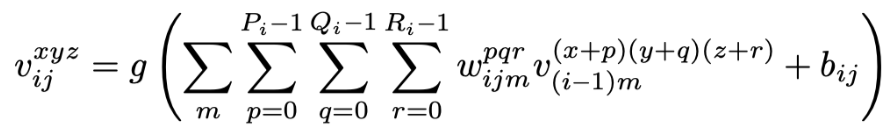
where m indexes the feature map in the $(i − 1)$th layer con- nected to the current (jth) feature map, and Pi and Qi are the height and the width of the spatial convolution kernel. Ri is the size of the kernel along toward spectral dimension, $w^{pqr}_{ijm}$ is the value of position$ (p, q, r)$ connected to the mth feature map, and bijis the bias of the jth feature map in the ith layer.
L2 Regularization of CNN + Dropout + ReLu– 防止过拟合
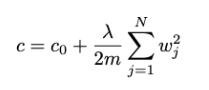
加入到Loss中鼓励参数尽量小
Dropout方法防止复杂的共同适应(co-adaptation).
Dropout和ReLU共同作用使很多神经元的输出变为0, 实现强大的基于稀疏的正则化深度网络, 解决HSI中的过拟合问题
VIRTUAL SAMPLE ENHANCED CNN–扩充样本方法
CNN需要很多的样本来训练大量的参数, 但HSI样本标记获取困难, 即样本数量少. 所以需要虚拟样本方法来扩充样本
2种扩充样本的方法
Although there are many other methods that can generate the virtual samples, the changing radiation and mixture-based methods are simple yet effective ways.
-
Changing Radiation-Based Virtual Samples
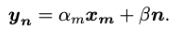
New virtual sample $y_n$ is obtained by multiplying a random factor and adding random noise to a training sample $x_m$
The training sample xmis a cube extracted from the hyper- spectral cube
αm indicates the disturbance of light intensity
β controls the weight of the random Gaussian noise n
-
Mixture-Based Virtual Samples
Because of the long distance between the object and the sensor, mixture is very common in remote sensing.???Inspired by the phenomenon, it is possible to generate a virtual sample yk from two given samples of the same class with proper ratios -
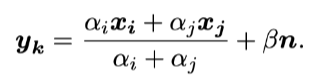
$x_i$and $x_j$are two training samples from the same class
Feature analyse 特征表示/特征分析
1D-CNN convolution kernal in HSI
第一层6个1*8卷积核, (a)随机初始化的权重, (b)学习到的权重
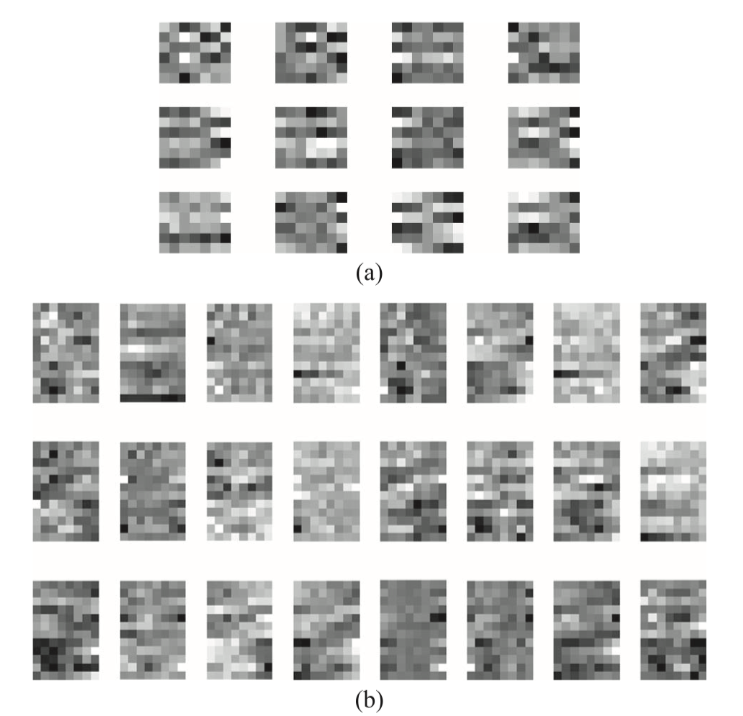
(a)学习到的第二层卷积核权重, 12个卷积核, 每个卷积核包含6*7个权重 (b)学习到的第三层卷积核权重, 24个卷积核, 每个卷积核包含12*8个权重
Q: 为什么6个1*8的核
A: 1个卷积核产生一种feature maps, 这个卷积核会在feature map特定不同位置内容作出反应,所以这个网络的结构应该在每层有如下特征图数量: 1 –> 6 –> 12 –> 24, 因此权值共享的意思即每个核在同一个特征图上用同样的权值,而每个核又有不一样的权重
因此可以说, CNN的学习过程: 更新卷积核参数(weights),就相当于是一直在更新所提取到的图像特征,以得到可以把图像正确分类的最合适的特征们。(一句话:更新weights以得到可以把图像正确分类的特征。)
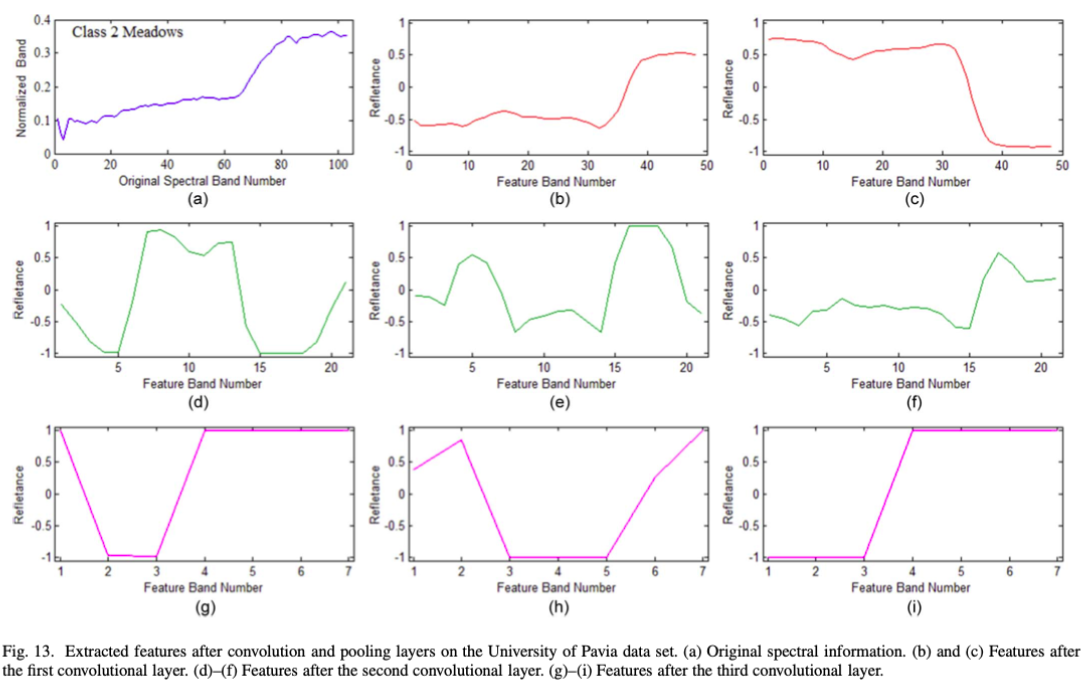
经过convolution和pooling提取特征后的波段信息:
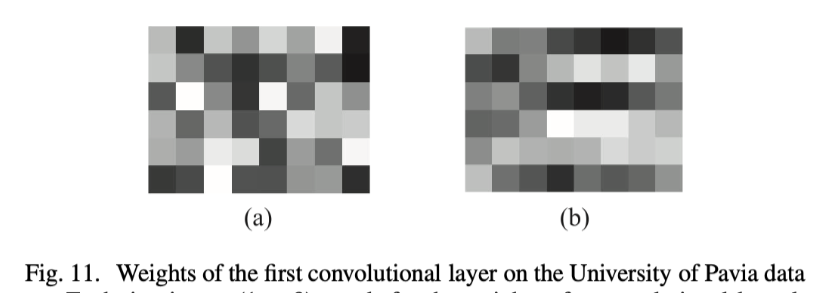
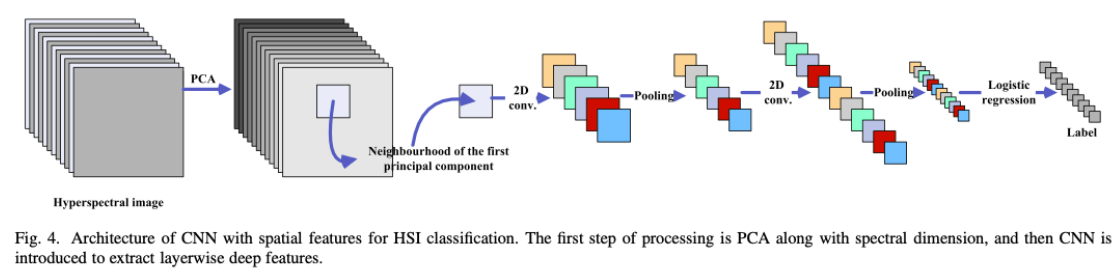
2D-CNN convolution kernal in HSI
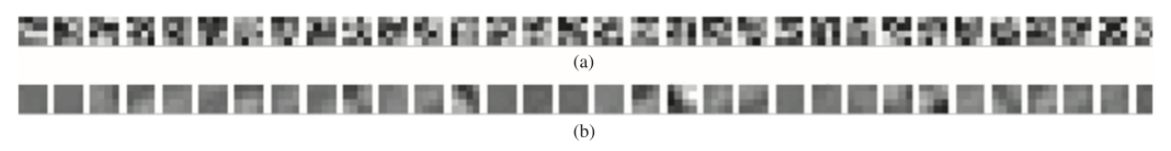
第一个卷积层对应的卷积核, 32个4*4的卷积核, 像素代表权重值,
(a)Pavia数据集随机出初始化的权重 (b)学习到的权重系数
特征提取

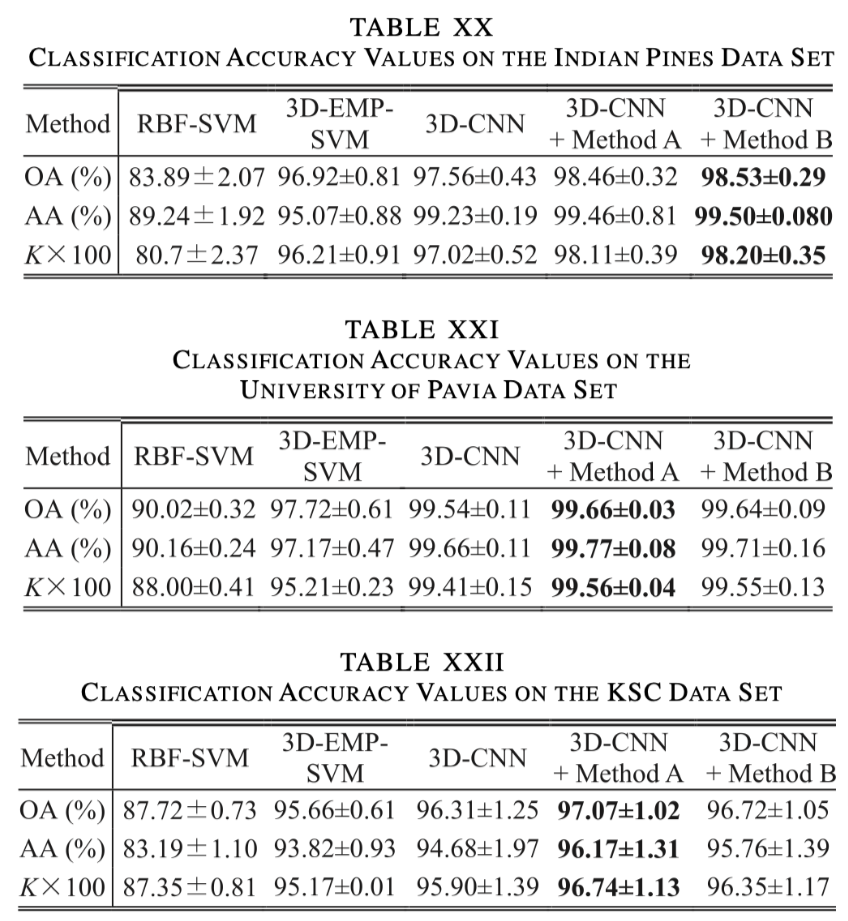
Result
-
Previous
论文学习 (19TGRS)A CNN With Multiscale Convolution and Diversified Metric for Hyperspectral Image Classification -
Next
Visual Representations(VR)综述